Tools | bat > cat
Bat
There are some eternal tools and cat is one of them. It has not appreciably changed much for an eternity. Recently I have stumbled upon a site called Terminal Trove. A tool missng from their posts is the tool bat. As a developer, and perhaps many Linux users, when I am using cat it is with a script or log snippet. However, without perks like colorization and line numbers it can be difficult to comprehend. This may lead a user to open it in vi or helix to get those benefits. What if you didn’t have to? That’s where bat enters the picture.
This is what bat looks like with a simple basic toml file.
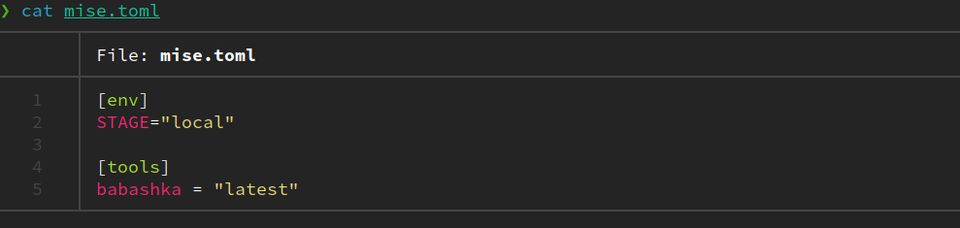
But bat is also capable of showing white space, is git-aware, and by default uses less for paging.
bat -A keyboards/ploopyco/ploopyco.h
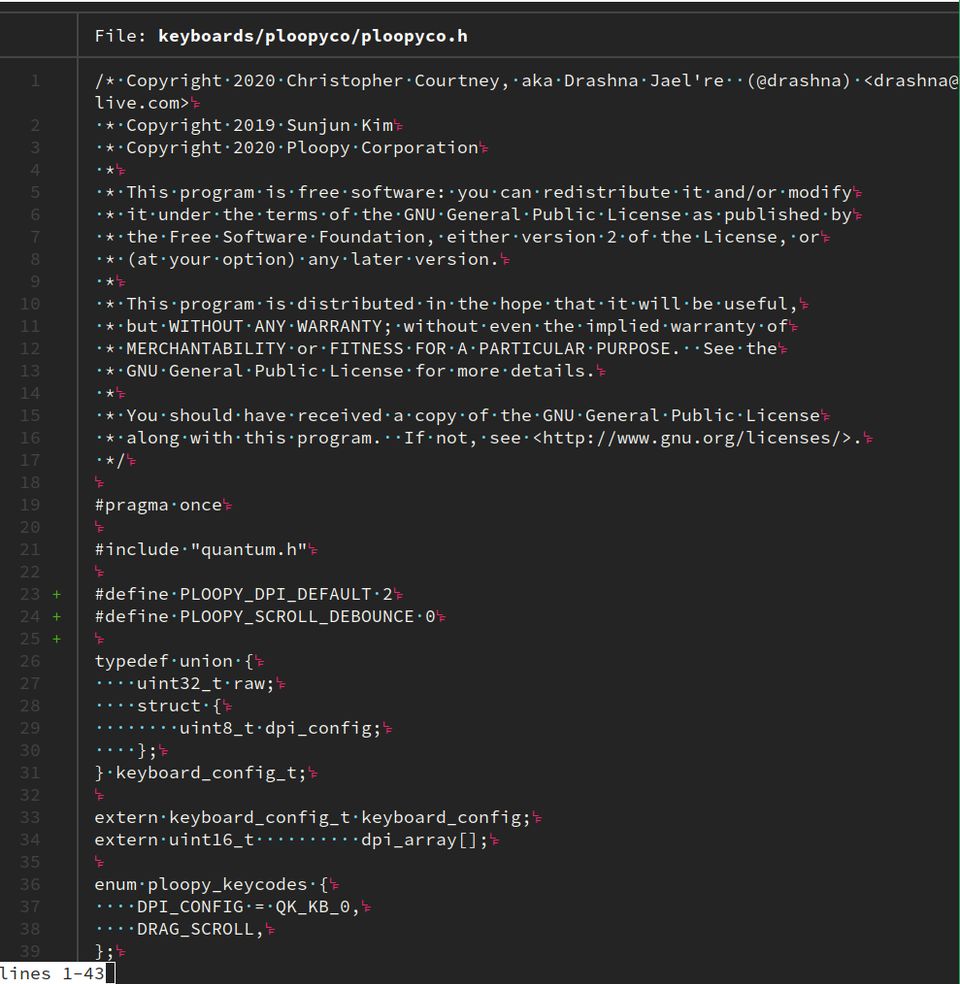
It also can read from stdin
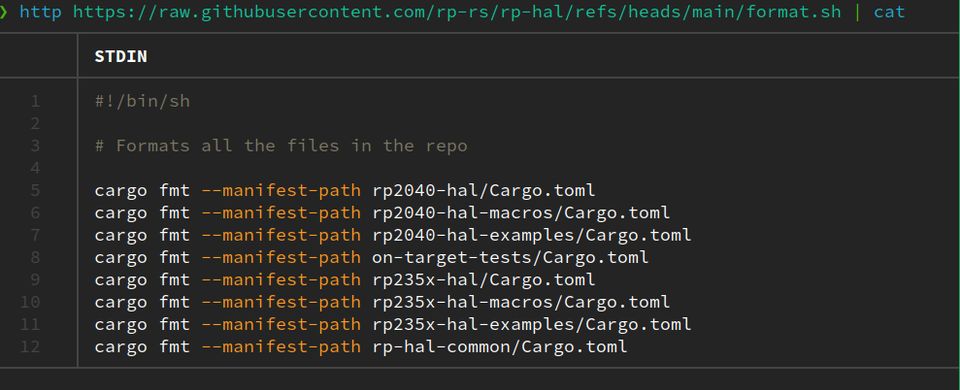
There is a wide range of options including those that allow you to customize the output, add themes, and return to default cat behavior for example.
❯ cat -h
A cat(1) clone with wings.
Usage: bat [OPTIONS] [FILE]...
bat <COMMAND>
Arguments:
[FILE]... File(s) to print / concatenate. Use '-' for standard input.
Options:
-A, --show-all
Show non-printable characters (space, tab, newline, ..).
--nonprintable-notation <notation>
Set notation for non-printable characters.
-p, --plain...
Show plain style (alias for '--style=plain').
-l, --language <language>
Set the language for syntax highlighting.
-H, --highlight-line <N:M>
Highlight lines N through M.
--file-name <name>
Specify the name to display for a file.
-d, --diff
Only show lines that have been added/removed/modified.
--tabs <T>
Set the tab width to T spaces.
--wrap <mode>
Specify the text-wrapping mode (*auto*, never, character).
-S, --chop-long-lines
Truncate all lines longer than screen width. Alias for '--wrap=never'.
-n, --number
Show line numbers (alias for '--style=numbers').
--color <when>
When to use colors (*auto*, never, always).
--italic-text <when>
Use italics in output (always, *never*)
--decorations <when>
When to show the decorations (*auto*, never, always).
--paging <when>
Specify when to use the pager, or use `-P` to disable (*auto*, never, always).
-m, --map-syntax <glob:syntax>
Use the specified syntax for files matching the glob pattern ('*.cpp:C++').
--theme <theme>
Set the color theme for syntax highlighting.
--list-themes
Display all supported highlighting themes.
--style <components>
Comma-separated list of style elements to display (*default*, auto, full, plain,
changes, header, header-filename, header-filesize, grid, rule, numbers, snip).
-r, --line-range <N:M>
Only print the lines from N to M.
-L, --list-languages
Display all supported languages.
-h, --help
Print help (see more with '--help')
-V, --version
Print versionInstall
The installation is straight forward. If you have the Rust toolchain installed building from source is an option.
cargo install --locked bat
Or using your package manager.
sudo zypper install bat bat-bash-completion bat-fish-completion
Integrate with Fish
As seen above there are fish completions available on OpenSUSE. One option to avoid muscle memory of typing cat vs bat would be to use a fish alias but that isn’t quite enough. There is a convinience flag that is just too much typing to get a pagerless output. This custom override for the cat command gives you a nice flag to get basic output as well as only overriding the cat command in interactive mode.
# Utilizes bat when in user shell to get prettier code prints but
# reverts to cat when not to prevent interfering with other scripts.
function cat --description "alias cat bat"
if status --is-interactive
# Initialize an empty list for the arguments
set -l args
for arg in $argv
# Replace '-a' with '--pager=never' in each argument, if applicable
if [ "$arg" = "-a" ]
set new_arg "--pager=never"
else
set new_arg $arg
end
# Add the processed argument (either modified or unchanged) to the args list
set args $args $new_arg
end
# In interactive mode, use bat
command bat $args
else
# In non-interactive mode, use cat
command cat $argv
end
endAs seen above the override only happens under interactive use. Additionally, it adds flag -a as an alias of --pager=never to save a few keystrokes. The command now to get plain cat output would be cat -a -p. Using the keyword command to execute cat and bat also maintains the correct fish completions based on the underlying command being run.
That is all for this installment. Look forward to more posts just like this.